OPPO Illustrates a Zero-Battery Future Powered by Wireless Signals with the Release of its Zero-Power Communication White Paper
26th January 2022, Kathmandu
In the near future, IoT devices will be able to harvest energy directly from Bluetooth, WiFi, and cellphone signals, resulting in excellent features such as smaller size, better durability, and lower cost.
Electronic tags are applied to locate the items without replacing or recharging the tag battery.
Meanwhile, every endangered migratory bird will be equipped with long-distance tracking devices. Therefore, the number of batteries will be significantly reduced.
Those are the futuristic scenes pictured in OPPO’s “Zero-Power Communication” white paper.
On January 20th, the OPPO Research Institute officially released its new white paper on Zero-Power Communication.
The paper examines the technical positioning of Zero-Power Communication technology in the context of current unmet demand in the IoT space while outlining a future roadmap for the technology to develop in coexistence with other communications systems of the future.
Zero-Power devices have excellent features such as being battery-free, highly compact, low power consumption, and low cost
The majority of portable electronic devices today rely on batteries as their power source. While battery technology has come a long way over the years, current battery technology still presents significant problems in terms of the overall size, production cost, lifespan, ease of use, and environmental friendliness of the batteries themselves.
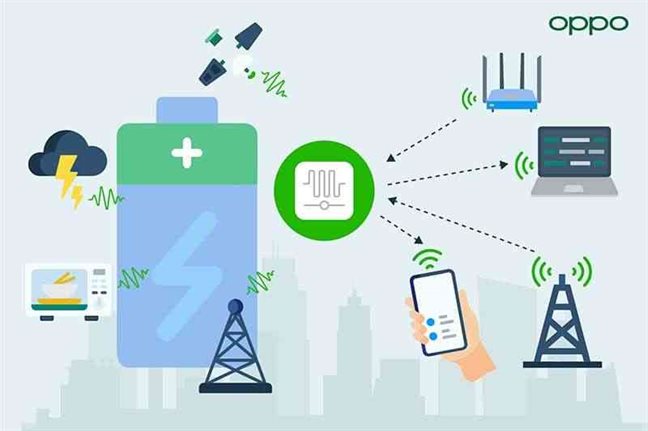
Zero-Power Communication technology avoids the need for batteries by harvesting ambient radiofrequency energy in the environment to generate power, resulting in highly compact, efficient, and low-cost devices.
Such properties have benefits in commercial applications such as warehousing, logistics, and agriculture and in wearable devices, smart homes, and other cutting-edge consumer applications.
“From the first to the fourth generations of mobile telecommunications technology, the telecommunications industry has gone through four technological leaps — from analog to digital, to data, and finally to broadband.
Each of these leaps has been designed to deliver faster data transmission rates; however, over the next decade, looking at 5G technology and even further afield, we no longer believe that data transmission will be as big a driver in telecommunications technology.
Instead, we believe that technology should evolve to deliver greater convenience and sustainable value for society as a whole.
Zero-Power Communications technology offers a means for electronics manufacturers to remove batteries from their products, reducing their costs and environmental impact in the process. As such, Zero-Power Communications is one of our core focus areas as we move into the B5G/6G generation,” said Henry Tang, OPPO’s Chief 5G Scientist.
While passive communication technology already exists today in radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, the current technology suffers from problems such as short communication distances, low efficiency, and small system capacity.
This presents significant challenges when applying RFID technology to specific or complex applications such as industrial sensor networks, low-cost and high-capacity logistics and warehousing, low-cost and low-power smart homes, and miniature wearable technology.
Unlike the traditional method, Zero-Power devices can harvest ambient radio signals broadcast from sources such as TV towers, FM radio towers, cellular base stations, and WiFi access points (APs) as their source of power.
After harvesting the energy from existing radio waves, the device can modulate ambient radio signals with its own information and transmit these signals outwards in a process known as backscattering communication.
When designing Zero-Power Communication networks, it is necessary to consider the coexistence of Zero-Power communication systems and existing 4G/5G systems apart from unlicensed and licensed bands.
Zero-Power Communication systems can be constructed in a framework that uses cellular communications, sideline communications, or both in hybrid.
Cellular-based Zero-Power Communications systems are best able to support industrial sensor network applications.
The sideline-based approach, on the other hand, is more suited to low-cost, short-range communications, such as wearables or smart home devices, where the devices can also be used to process the data they receive.
A hybrid approach using both cellular and sideline communication methods will further allow developers to unlock more applications using Zero-Power Communications systems.
Zero-Power Communication mainly utilizes RF power harvesting, backscattering, and low-power computing technology
OPPO has already successfully built its own Zero-Power Communication system and demonstrated the feasibility of the concept as a viable approach to future communications networks.
In addition to its own innovation, OPPO is also taking the lead in promoting the Zero-Power Communication standard, including proposing Zero-Power Communication research projects to 3GPP and presenting its findings during industry conferences such as FuTURE and ICCC.
At the IMT-2030 6G Vision workshop in September 2021, OPPO initiated and organized a Zero-Power Communication Forum, inviting academic and industry organizations to discuss applications, technical requirements, and key technologies in Zero-Power Communication.
As the industry moves towards 6G technology, OPPO believes that Zero-Power Communication will work with other core technologies such as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces, Symbiotic Radio, Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA), and AI to unleash the full potential of 6G.
OPPO has unveiled two white papers to continue researching cutting-edge communication technologies.
Before the Zero-Power Communication White Paper, OPPO also published its 6G AI-Cube Intelligent Networking White Paper in its continued research into cutting-edge communication technologies.
In line with its brand mission of ‘Technology for mankind, kindness for the world, ‘OPPO is targeting to release commercial Zero-Power Communication technology within the next 3 to 5 years as it continues to build smarter, more convenient, and greener communications systems.